
Research News
Research News
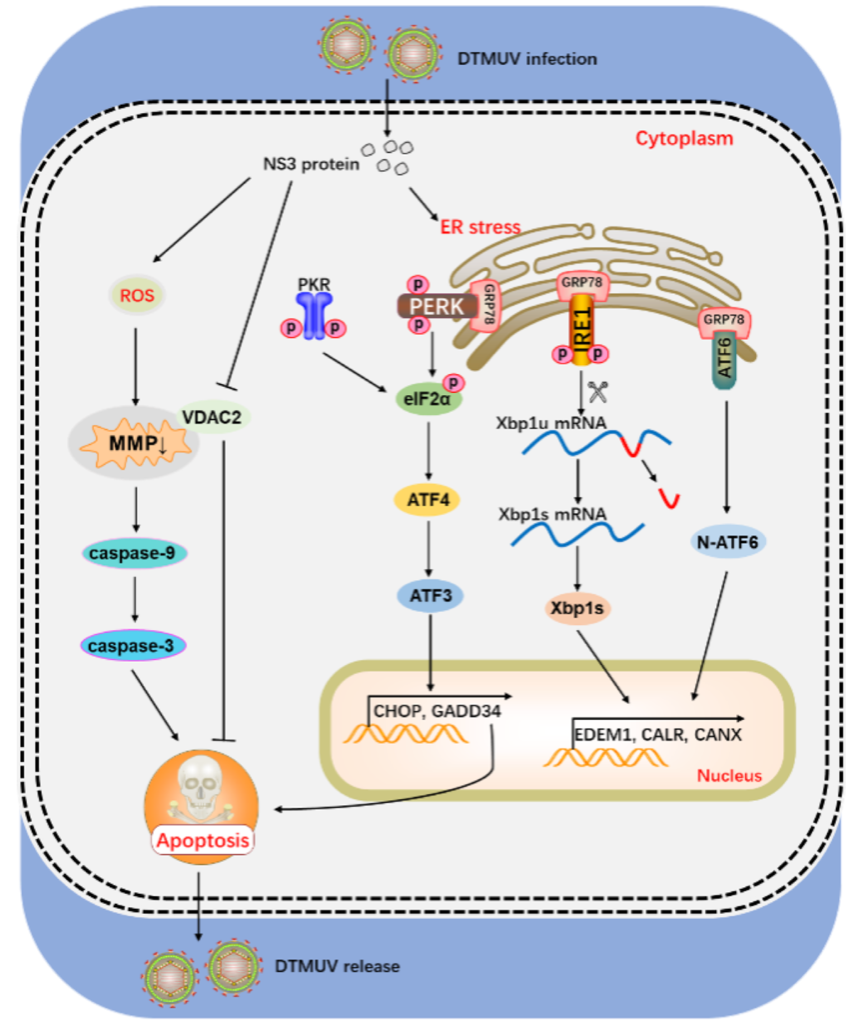
Duck Tembusu virus NS3 protein induces apoptosis by activating the PERK/PKR pathway and mitochondrial pathway
Duck Tembusu virus (DTMUV) infection causes severe infectious diseases in poultry and can induce apoptosis in host cells. In this study, the mechanisms underlying DTMUV-induced apoptosis were investigated. First, DTMUV infection can activate the endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS), and administration of the ERS inhibitor 4-phenylbutyric acid can protect cells from DTMUV-induced apoptosis, indicating that ERS is involved in DTMUV-induced apoptosis. Interestingly, suppression of either apoptosis or ERS led to impaired DTMUV proliferation. Then, we found that DTMUV activated three branches of unfolded protein response signaling [RNA-activated protein kinase-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK), inositol-requiring enzyme 1, and activating transcription factor 6] in duck embryo fibroblasts. Further study revealed that activation of PERK-eukaryotic initiation factor 2α up-regulated CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein and DNA damage-inducible protein 34, which subsequently promoted apoptosis. Moreover, we found that among the DTMUV viral proteins, the nonstructural protein 3 (NS3) is the main inducer of apoptosis. On the one hand, the PERK/PKR pathway is involved in the NS3-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. On the other hand, NS3 interacts with voltage-dependent anion channel 2 (VDAC2) and inhibits the anti-apoptotic protein VDAC2 to induce apoptosis, which is accompanied by the depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential and accumulation of intracellular reactive oxygen species. This study provides a theoretical basis for revealing the pathogenic mechanism of DTMUV infection and lays a foundation for finding antiviral targets.
https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.01497-23




 028-86296382
028-86296382  No. 211 Huimin Road, Wenjiang District, Chengdu, Sichuan Province
No. 211 Huimin Road, Wenjiang District, Chengdu, Sichuan Province 