
Research News
Research News
Innovative Progress in Porcine Deltacoronavirus Oral Vaccine Research at the Research Center for Swine Disease
On December 12, 2014, the Research Center for Swine Disease at Sichuan Agricultural University published a research paper titled "Development and immunogenicity evaluation of attenuatedSalmonella Typhimuriumdelivering porcine Deltacoronavirus S1 gene" inInternational Journal of Biological Macromolecules(a top-tier journal in the Chinese Academy of Sciences, IF= 7.7). This study firstly reports the use of the attenuatedSalmonellastrain SL7207 as a vector to develop an oral vaccine SL7207(pVAX1-S1) delivering the S1 gene of PDCoV, and provides a comprehensive evaluation of the immunogenicity, protective efficacy, and potential applications of SL7207(pVAX1-S1).

Porcine Deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) is an enteropathogenic coronavirus that primarily infects piglets, causing watery diarrhea, vomiting, dehydration, and death in neonatal piglets. First reported in Hong Kong in 2012, PDCoV has since been identified in most pig-producing countries worldwide. It has become one of the leading viral causes of diarrhea in piglets in China, threatening the development of the swine industry. PDCoV has broad cross-species transmission potential, with reports indicating its ability to infect calves, chickens, turkeys, mice, and other animals. Additionally, some studies suggest a potential risk of human infection. Since PDCoV is an enteric pathogen, the development of an oral vaccine against it holds significant practical value.
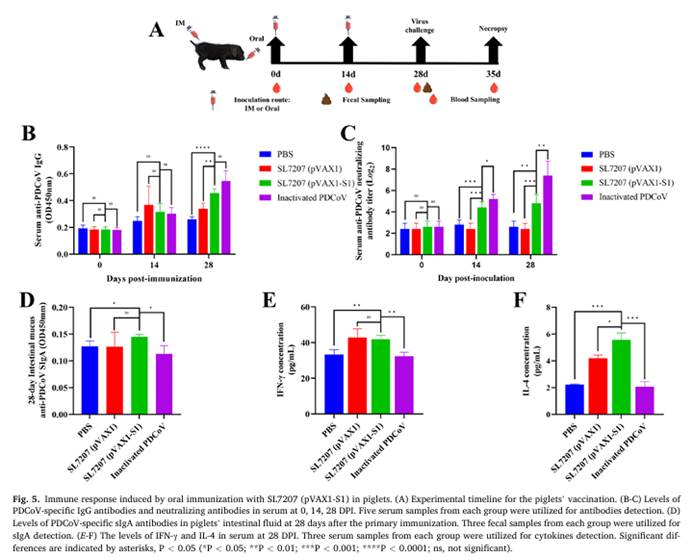
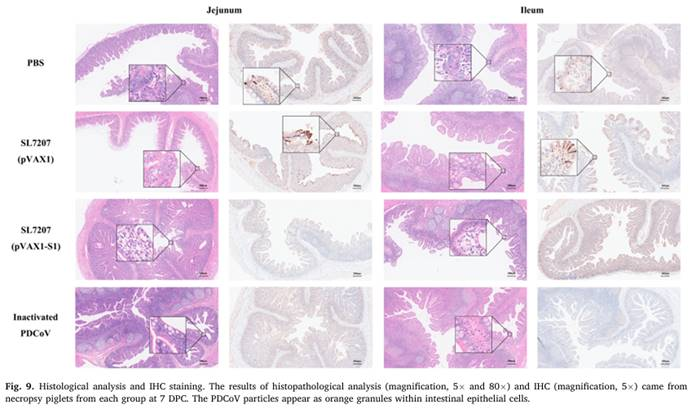
This study first constructed a recombinant eukaryotic expression vector, pVAX1-S1, which expresses the S1 gene, using genetic recombination technology. The recombinant attenuatedSalmonellastrain SL7207 (pVAX1-S1) was then generated. The antigen presentation capability and biological properties of SL7207 (pVAX1-S1) were comprehensively evaluated through Western blot (WB), immunofluorescence assay (IFA), growth curve analysis, and safety assessments. Subsequently, the oral immunogenicity of SL7207 (pVAX1-S1) was evaluated in mice and piglets. The results demonstrated that oral administration of SL7207 (pVAX1-S1) induced strong humoral and cellular immune responses in both mice and piglets. Protection studies in piglets challenged with PDCoV showed that, compared to the control group, both the SL7207 (pVAX1-S1) group and the inactivated vaccine group provided clinical protection. The challenged piglets in these groups exhibited milder diarrhea, less severe intestinal lesions, and lower fecal virus shedding compared to the control group. This study provides important insights for further exploration or improvement of novel PDCoV oral vaccine.


Junpeng Yang (MSC 2022), Rui Chen (PhD 2020) and Mengke Sun (PhD 2023) are the co-first authors of this paper, and Prof. Xiaobo Huang is the corresponding author. This research was supported by Sichuan International Science and Technology Innovation Cooperation Project (No.2021YFH0153), the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (No.2021ZDZX0010), the Major Science and Technology Project of Yunnan Province (No.202102AE090039), Biohazard Prevention and Control Fund of Chenghua Pig Protection Base (No.ZZSS-2024-193), and the Innovation and Demonstration of Industry and Education Integration in Feed Industrial Chain Transformation and Upgradation, Sichuan Province, China.




 028-86296382
028-86296382  No. 211 Huimin Road, Wenjiang District, Chengdu, Sichuan Province
No. 211 Huimin Road, Wenjiang District, Chengdu, Sichuan Province 